We deliver to you every day from 7:00 to 23:00
The best discounts this week
Every week you can find the best discounts here.
Can Painkillers Cause Dizziness?
Painkillers are commonly used to relieve pain and discomfort, but many people are unaware that they can also have side effects, including dizziness. This article explores the relationship between painkillers and dizziness, providing valuable information on what causes dizziness, the types of painkillers that might lead to this side effect, and how to manage it. With regular updates, this guide will give you the most accurate and in-depth knowledge on this topic.
What Is Dizziness?
Dizziness is a broad term used to describe feelings of lightheadedness, vertigo (the sensation of spinning), or unsteadiness. It can range from mild to severe and is often caused by a disruption in the body’s balance systems. The inner ear, blood pressure, and neurological systems all play a role in balance, and any disturbance in these systems can cause dizziness.
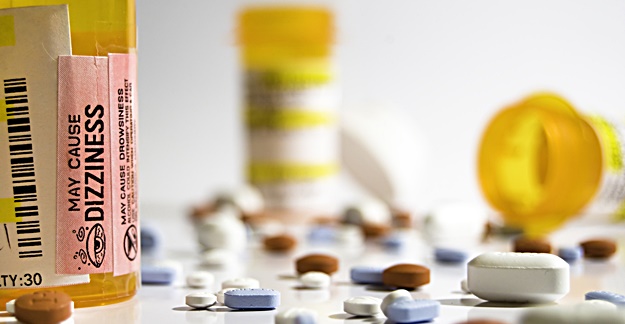
If you have experienced dizziness after taking painkillers, it’s important to understand why this might happen and what to do about it.
How Do Painkillers Affect the Body?
Painkillers work by blocking the pain signals in your brain or reducing inflammation. While effective in pain management, they can also interact with other bodily systems, sometimes leading to side effects. Some painkillers affect the nervous system, blood pressure, and balance mechanisms, which can result in dizziness.
The Different Types of Painkillers
Painkillers come in different forms, and each type can have varying effects on the body. Some of the most common categories include:
-
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs, such as ibuprofen and aspirin, are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. They are often associated with gastrointestinal side effects but can also cause dizziness in some individuals.
-
Opioids: Opioids, like morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone, are strong painkillers that can lead to dizziness, especially when used in high doses or for prolonged periods. Opioids depress the central nervous system, which can affect balance and cause lightheadedness.
-
Acetaminophen: Known commonly as Tylenol, acetaminophen is a widely used over-the-counter painkiller. While it is less likely to cause dizziness compared to other painkillers, some individuals may still experience this side effect, particularly if combined with other medications.
Each type of painkiller can affect the body in unique ways, so understanding these distinctions is key to managing potential side effects like dizziness.
Why Do Painkillers Cause Dizziness?
Several factors contribute to the dizziness caused by painkillers. Here are the main reasons:
1. Central Nervous System Depression
Some painkillers, especially opioids, act on the central nervous system (CNS) to reduce pain. This can lead to sedation, drowsiness, and dizziness, especially when standing up quickly. The CNS depression slows down brain activity and can impair the body’s balance mechanisms.
2. Changes in Blood Pressure
Painkillers like NSAIDs and opioids can affect blood pressure by either raising or lowering it. A sudden drop in blood pressure, known as orthostatic hypotension, is a common cause of dizziness. This happens when you stand up quickly and your body can’t adjust to the change in position, leading to feelings of lightheadedness.
3. Dehydration
Some painkillers, particularly NSAIDs, can lead to dehydration. Dehydration is a common cause of dizziness because it affects the body’s ability to maintain proper blood flow and fluid balance. This can make you feel lightheaded, especially if you’re already feeling unwell.
4. Inner Ear Disruption
Certain painkillers can affect the inner ear, which plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. If the inner ear becomes disrupted or inflamed, dizziness may occur as a side effect. This is more likely to happen with long-term use of specific pain medications.
Common Painkillers That Can Cause Dizziness
Not all painkillers lead to dizziness, but some are more likely to cause this side effect. Here are some of the most common culprits:
1. Opioids (e.g., Morphine, Oxycodone)
Opioids are powerful painkillers that can cause severe dizziness, especially when taken in large doses or combined with other depressant medications. The central nervous system (CNS) depression they cause is the primary reason for dizziness. Long-term use can exacerbate this effect.
2. NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen, Naproxen)
Although NSAIDs are generally considered safe for short-term pain relief, they can cause dizziness, particularly if used excessively. The effect is usually due to changes in blood pressure and kidney function.
3. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
While acetaminophen is considered safer and less likely to cause dizziness than other painkillers, some individuals may experience mild dizziness, especially when used in high doses.
How to Manage Dizziness Caused by Painkillers
If you experience dizziness after taking painkillers, there are several steps you can take to manage the side effect:
1. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can exacerbate dizziness, so it’s important to drink plenty of water. This is especially true if you’re taking painkillers like NSAIDs that may contribute to dehydration.
2. Take Medications with Food
Taking painkillers on an empty stomach can lead to side effects like dizziness. Try taking your medication with food to minimize this risk.
3. Avoid Standing Up Too Quickly
If you experience dizziness from low blood pressure, try to stand up slowly to allow your body to adjust. This can help prevent lightheadedness and prevent falls.
4. Consult Your Doctor
If dizziness persists or worsens, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. They may be able to adjust your dosage or recommend alternative pain management options that don’t cause dizziness.
When Should You Be Concerned About Dizziness?
While dizziness caused by painkillers is usually temporary, there are instances when it can be a sign of something more serious. Seek medical help immediately if:
-
You experience severe dizziness or fainting.
-
Dizziness is accompanied by chest pain or difficulty breathing.
-
You feel confused or have trouble staying awake.
These could be signs of an adverse reaction to the medication or another underlying condition.
FAQs About Painkillers and Dizziness
1. Can all painkillers cause dizziness?
No, not all painkillers cause dizziness. While opioids and NSAIDs are the most common culprits, acetaminophen is less likely to cause dizziness, though it can still happen in some individuals.
2. How long does dizziness last after taking painkillers?
Dizziness usually lasts only a few hours after taking painkillers, but the duration can vary depending on the type of painkiller and your body’s response. If dizziness persists, contact your doctor.
3. What should I do if I feel dizzy after taking painkillers?
If you feel dizzy after taking painkillers, it’s important to sit or lie down and avoid sudden movements. Drink water and take your medication with food if possible. If dizziness persists, consult a healthcare provider.
4. Are there any painkillers that are less likely to cause dizziness?
Acetaminophen is generally less likely to cause dizziness compared to opioids or NSAIDs. However, if dizziness is a concern, consult with your doctor for alternative options.
Conclusion
Painkillers are an essential part of managing pain, but they can come with side effects, including dizziness. Understanding the reasons why painkillers can cause dizziness and how to manage it is crucial for your health and safety. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about the side effects of painkillers and take the necessary steps to minimize their impact.
By staying informed and following the proper precautions, you can enjoy the benefits of pain relief without compromising your well-being.
For more information on pain management and other healthcare topics, visit DUYTHIN.DIGITAL.