We deliver to you every day from 7:00 to 23:00
The best discounts this week
Every week you can find the best discounts here.
Best Headache Medication: Finding Effective Relief
Headaches can be one of the most disruptive and painful conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. Whether it’s a mild tension headache or a severe migraine, finding effective relief is crucial to maintaining your daily routine. In this article, we will explore the best headache medications, how they work, and the various options available to help you manage and treat headaches.

Understanding Headaches
Headaches are characterized by pain in the head, scalp, or neck area. There are several types of headaches, and each type may require different treatment methods. The most common types include:
-
Tension headaches: These are the most common type and are usually caused by stress, fatigue, or poor posture.
-
Migraine headaches: These are more intense and often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
-
Cluster headaches: These are rare but extremely painful and occur in cycles or clusters, often on one side of the head.
-
Sinus headaches: These are caused by inflammation in the sinuses and typically accompany cold or allergy symptoms.
Identifying the type of headache you’re experiencing is essential in choosing the right medication for effective treatment.
Over-the-Counter Headache Medications
Most headaches can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medications. These are easily accessible and come in a variety of forms, including tablets, gels, and powders. Here are the most common OTC options for headache relief:
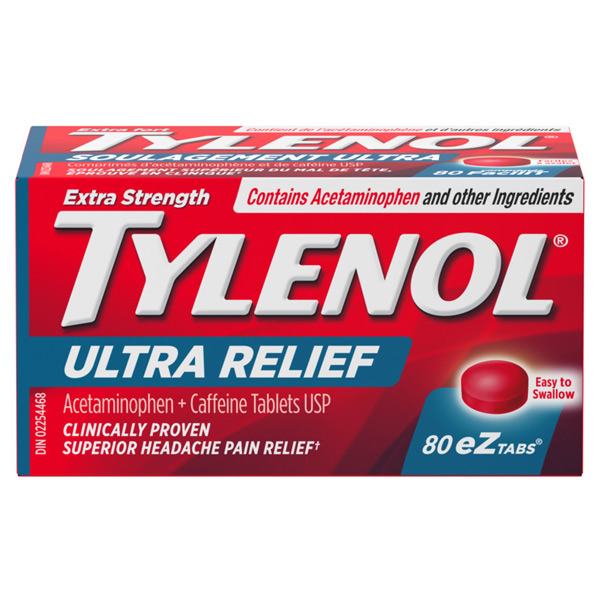
1. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Acetaminophen is one of the most commonly used OTC pain relievers. It’s effective for treating mild to moderate headaches and is often recommended for people who cannot take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) due to stomach issues.
-
Pros: Gentle on the stomach, widely available.
-
Cons: Not as effective for severe headaches or migraines.
Acetaminophen works by blocking the production of chemicals in the brain that signal pain, making it a good option for tension headaches or mild migraines.
2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve), are popular choices for treating headaches. They work by reducing inflammation, which can help relieve pain associated with conditions like sinus headaches or tension headaches.
-
Pros: Effective for a variety of headache types, reduces inflammation.
-
Cons: Can irritate the stomach or cause other side effects when used frequently.
3. Combination Medications
Some OTC medications combine acetaminophen, caffeine, and aspirin to enhance the effects on headache pain. One popular example is Excedrin, which is specifically formulated for migraine relief.

-
Pros: Often more effective for migraine headaches due to the combination of ingredients.
-
Cons: Caffeine can cause side effects like jitteriness or insomnia if taken in excess.
These combination medications are widely available and highly effective for treating moderate to severe headaches.
Prescription Headache Medications
While OTC medications are often sufficient for treating headaches, some people require stronger treatments. Prescription medications are available for people with more severe or chronic headaches, including migraines and cluster headaches.
1. Triptans
Triptans, such as sumatriptan (Imitrex), are a class of drugs specifically designed to treat migraines. They work by constricting blood vessels and blocking pain pathways in the brain. Triptans are highly effective for acute migraine attacks.
-
Pros: Highly effective for migraines, fast-acting.
-
Cons: Can cause side effects like dizziness or nausea, and they’re not suitable for people with certain medical conditions (e.g., heart disease).
2. Ergot Alkaloids
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older migraine treatments that work by narrowing blood vessels to reduce migraine pain. They are sometimes used when triptans are ineffective.
-
Pros: Effective for some migraine sufferers.
-
Cons: Can cause side effects, such as nausea, and are less commonly used due to better options available.
3. Anti-Nausea Medications
For people with migraines that cause nausea, anti-nausea medications like metoclopramide (Reglan) or prochlorperazine (Compazine) may be prescribed. These help manage the nausea and vomiting that often accompany severe migraines.
4. Corticosteroids
For extremely severe or persistent headaches, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. These are typically only used for short periods due to potential side effects.
Preventive Medications for Chronic Headaches
Some people suffer from chronic headaches, where migraines or tension headaches occur frequently. In these cases, preventive medications may be necessary to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
1. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers, such as propranolol (Inderal), are commonly prescribed for people who experience frequent migraines. They help regulate blood pressure and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks by preventing the blood vessels from constricting too much.
-
Pros: Effective for preventing migraines.
-
Cons: Can cause fatigue or dizziness.
2. Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, can also be used as preventive treatments for headaches. These medications work by increasing levels of serotonin in the brain, which helps regulate pain pathways.
-
Pros: Effective for chronic headaches and migraines.
-
Cons: Can cause drowsiness or weight gain.
3. Anti-Seizure Medications
Topiramate (Topamax) and valproate are anti-seizure medications that have also been found to be effective in preventing migraines. They work by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain.
-
Pros: Prevents chronic migraines.
-
Cons: Potential side effects include memory issues or mood changes.
Lifestyle Tips for Headache Prevention
While medications play an important role in headache relief, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency of headaches and improve overall health.
1. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration is a common trigger for headaches, particularly migraines. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help prevent dehydration and reduce the risk of headaches.
2. Manage Stress
Stress is a major trigger for tension headaches and migraines. Practicing stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can significantly reduce headache frequency.
3. Regular Sleep Patterns
Getting consistent, quality sleep is essential for headache prevention. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night and establish a regular sleep schedule.
4. Avoid Known Triggers
Certain foods, drinks, or environmental factors can trigger headaches. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, processed foods, and bright lights. Identifying and avoiding your triggers can significantly reduce headaches.
FAQs
1. What is the best medication for a severe migraine?
For severe migraines, triptans like sumatriptan (Imitrex) are often the most effective treatment. For those who cannot take triptans, ergot alkaloids or anti-nausea medications may help.
2. Can over-the-counter medications help prevent migraines?
Over-the-counter medications like Excedrin can help alleviate the pain of a migraine once it starts, but for chronic migraine sufferers, preventive medications such as beta-blockers or antidepressants are usually more effective.
3. Is it safe to use headache medication every day?
Using headache medication frequently can lead to medication overuse headaches. It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and not exceed the recommended dosage. If you find yourself needing pain relief daily, consult your healthcare provider.
4. Can lifestyle changes help with headache prevention?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can play a significant role in preventing headaches.
Conclusion
When it comes to finding the best headache medication, the right choice depends on the type, severity, and frequency of your headaches. From over-the-counter options like acetaminophen and NSAIDs to prescription treatments such as triptans and beta-blockers, there are many options to explore. Additionally, adopting healthy lifestyle changes can help reduce the occurrence of headaches. If you’re struggling with chronic or severe headaches, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for you.