We deliver to you every day from 7:00 to 23:00
The best discounts this week
Every week you can find the best discounts here.
Chronic Migraine Drugs: The Best Treatment Options for Long-Term Relief
Chronic migraines are a severe and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike occasional headaches, chronic migraines occur frequently, often with a range of debilitating symptoms. If you suffer from chronic migraines, you know how they can disrupt daily life, making it hard to work, socialize, or enjoy activities. Fortunately, there are various chronic migraine drugs available that can provide effective relief.
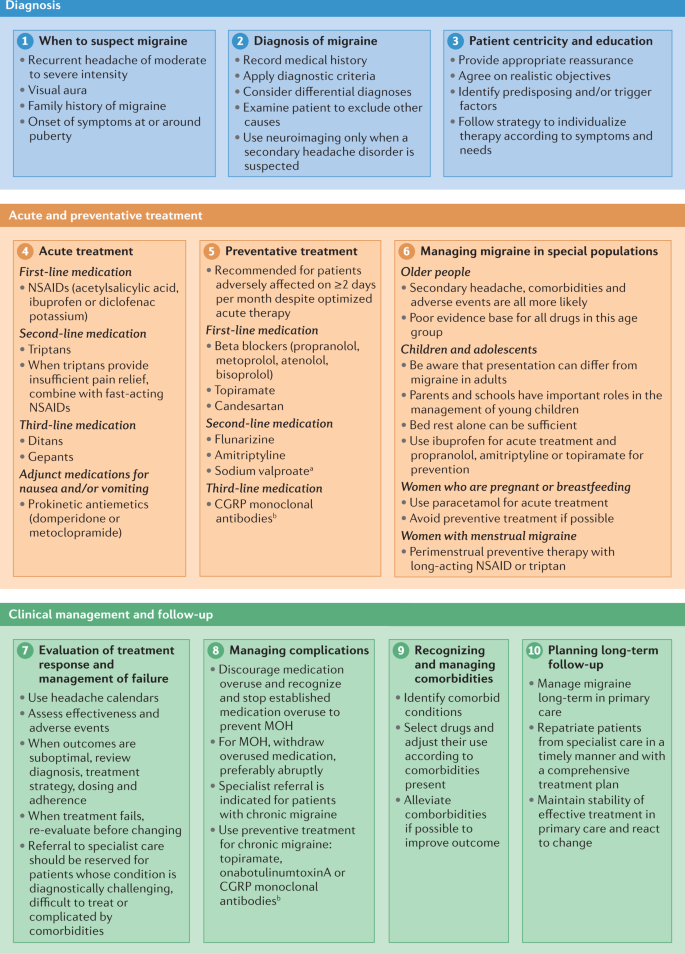
What Are Chronic Migraines?
A chronic migraine is defined as a headache that occurs 15 or more days per month for at least three months, with at least 8 of those days involving migraine-like symptoms. Chronic migraines are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and heightened sensitivity to light, sound, and smells. These types of headaches can last anywhere from 4 hours to several days, making them particularly challenging to manage.
Symptoms of Chronic Migraines
The symptoms of chronic migraines can vary, but they generally include:
-
Intense throbbing or pulsing pain on one side of the head.
-
Nausea or vomiting.
-
Sensitivity to light, sound, and smells.
-
Aura symptoms (visual disturbances like flashing lights or blind spots).
-
Neck pain or stiffness.
If you experience these symptoms regularly, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
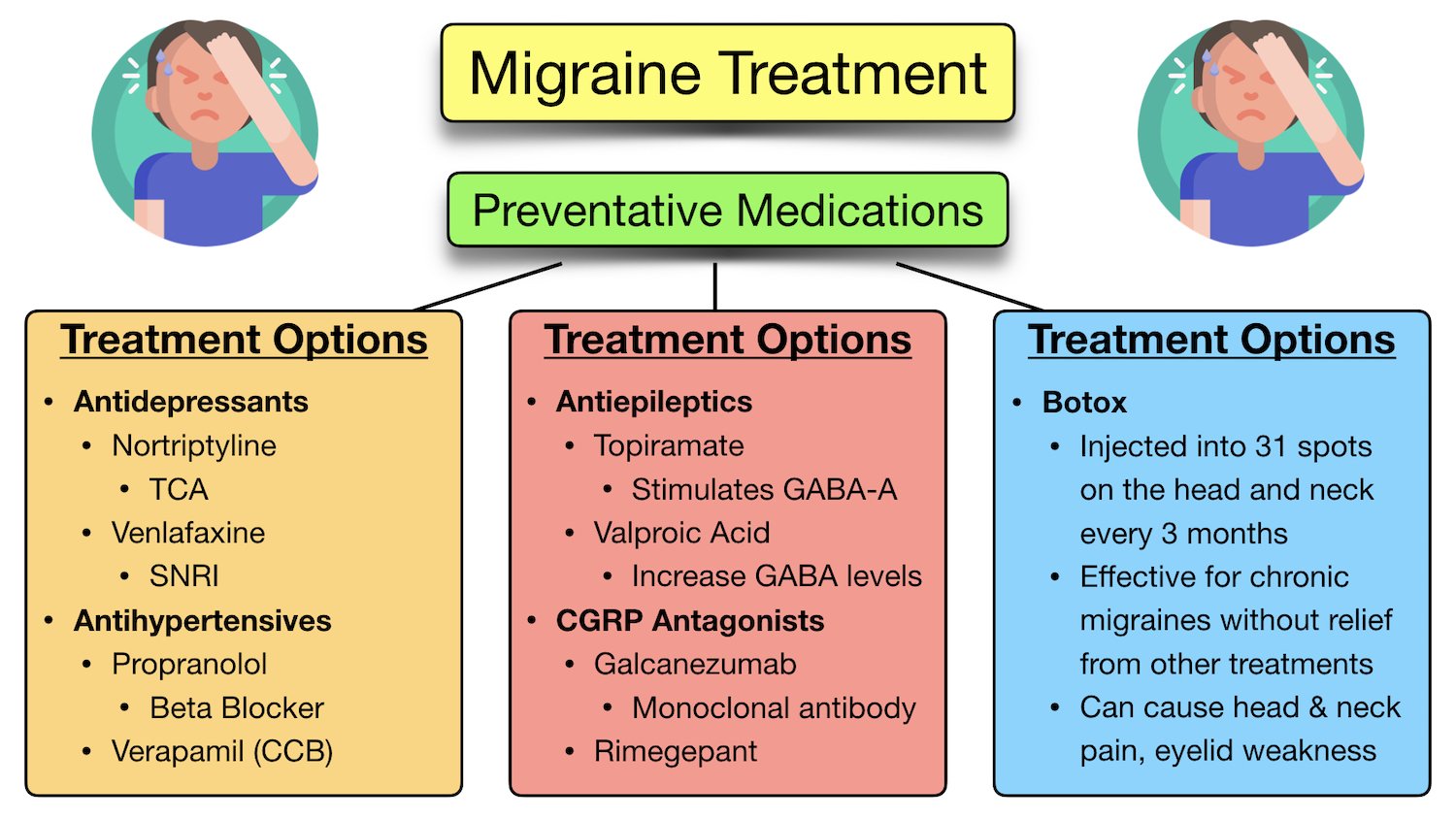
The Role of Medications in Chronic Migraine Treatment
While there is no permanent cure for chronic migraines, medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms and reducing the frequency and severity of migraines. Treatment options generally fall into two categories: acute treatments for immediate relief and preventive treatments that reduce the likelihood of future migraines.
Acute Migraine Treatments
Acute treatments are designed to relieve the pain and symptoms of a migraine once it has already started. These medications can be taken at the onset of a migraine attack to stop or lessen the pain.
1. Triptans
Triptans are a class of drugs commonly used to treat migraines. They work by constricting blood vessels in the brain, reducing inflammation, and blocking pain pathways. Some popular triptans include:
-
Sumatriptan (Imitrex)
-
Rizatriptan (Maxalt)
-
Zolmitriptan (Zomig)
Triptans are highly effective for many people, but they may not work for everyone and may cause side effects such as dizziness or nausea.
2. Pain Relievers
For less severe migraine attacks, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil), or aspirin may be effective. These medications help reduce pain and inflammation. However, they should not be overused, as excessive consumption can lead to medication overuse headaches.
3. Anti-Nausea Medications
Migraines often cause nausea and vomiting. Anti-nausea medications such as metoclopramide (Reglan) or prochlorperazine (Compazine) can help manage these symptoms, providing relief from the overall migraine experience.
4. Ergotamines
Ergotamines, like ergotamine (Cafergot), are another class of drugs used to treat migraines. They work by narrowing blood vessels around the brain. However, they are not commonly used today due to the availability of newer medications that have fewer side effects.
Preventive Migraine Treatments
Preventive treatments are designed to reduce the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraines. These medications are taken regularly, often daily, to reduce the likelihood of a migraine attack.
1. Botox Injections
Botox (botulinum toxin) is a well-known treatment for chronic migraines. It involves injecting small doses of the toxin into specific areas of the head and neck to block the release of pain-causing chemicals. Studies have shown that Botox injections can significantly reduce the frequency of chronic migraines in many people.
2. CGRP Inhibitors
CGRP inhibitors are a newer class of medications used for migraine prevention. CGRP (Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide) is a molecule involved in the process of migraine attacks. By blocking CGRP, these drugs help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Some CGRP inhibitors include:
-
Erenumab (Aimovig)
-
Fremanezumab (Ajovy)
-
Galcanezumab (Emgality)
These medications are typically administered as monthly injections and have shown excellent results in clinical trials.
3. Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants, particularly amitriptyline (Elavil), have been found effective in preventing migraines. These medications work by altering the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, which may help reduce migraine frequency.
4. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers, such as propranolol (Inderal), are often used to prevent migraines, particularly for those with high blood pressure. They work by affecting blood flow and reducing the occurrence of migraine attacks.
5. Anti-Seizure Medications
Anti-seizure medications, like topiramate (Topamax) or valproic acid (Depakote), are sometimes prescribed for migraine prevention. These drugs help stabilize electrical activity in the brain and can significantly reduce migraine frequency.
Choosing the Right Chronic Migraine Drug
The best chronic migraine drug for you will depend on several factors, including the severity of your migraines, your medical history, and how you respond to different treatments. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that may include a combination of medications.
Consult a Healthcare Provider
Before starting any treatment, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider to ensure that the medication is appropriate for your specific condition. Your doctor will evaluate your symptoms and suggest the best treatment plan, which may include lifestyle changes in addition to medications.
FAQs About Chronic Migraine Drugs
1. Are chronic migraine drugs safe?
Most chronic migraine drugs are safe when used as prescribed. However, there can be side effects. It’s essential to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before starting a treatment plan.
2. How long does it take for chronic migraine drugs to work?
Some medications, like triptans, work quickly to relieve pain, while others, such as CGRP inhibitors or Botox, may take a few weeks to show full effects.
3. Can lifestyle changes help manage chronic migraines?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and avoiding known migraine triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of chronic migraines.
4. Can chronic migraines be cured with medication?
While there is no cure for chronic migraines, medications can significantly reduce their frequency and severity. A combination of preventive and acute treatments is often the most effective approach.
Conclusion
Managing chronic migraines can be challenging, but with the right combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the impact they have on your life. Whether it’s triptans for immediate relief or CGRP inhibitors for long-term prevention, there are various effective treatments available. Work with your healthcare provider to find the best option tailored to your needs, and take steps to reduce triggers and improve your overall quality of life.