We deliver to you every day from 7:00 to 23:00
The best discounts this week
Every week you can find the best discounts here.
Pain Management Drugs: Comprehensive Guide to Effective Pain Relief
Pain is one of the most common reasons people seek medical attention. Whether caused by injury, illness, or chronic conditions, managing pain is crucial for improving quality of life. Fortunately, there are various pain management drugs designed to provide relief, each with specific benefits and risks. In this article, we will explore the different types of pain management drugs, their uses, and important considerations when using them.
What Are Pain Management Drugs?
Pain management drugs are medications used to alleviate pain. These drugs can be categorized into several types, including over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, prescription pain medications, and alternative treatments. Pain medications work by blocking pain signals from reaching the brain or by altering the brain’s perception of pain.
Common Types of Pain Management Drugs
Pain management drugs can be divided into different classes based on their mechanisms of action and the severity of pain they treat. Below are the most common types:
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are one of the most widely used pain management drugs. They are commonly prescribed for mild to moderate pain and work by reducing inflammation, which is often the source of pain. These include drugs like ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin.-
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): Effective for treating headaches, menstrual cramps, and muscle pain.
-
Aspirin: Commonly used for inflammation and pain relief from conditions like arthritis.
-
Naproxen (Aleve): Known for its longer-lasting effects compared to ibuprofen.
-
-
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Unlike NSAIDs, acetaminophen works by blocking the brain’s pain receptors, making it an effective pain reliever for conditions like headaches, fever, and mild aches. It is commonly used for mild to moderate pain but does not address inflammation.-
Tylenol is the most common over-the-counter form of acetaminophen.
-
It is generally considered safer for individuals who cannot take NSAIDs due to stomach issues or other complications.
-
-
Opioids
Opioids are powerful pain relievers prescribed for severe pain, such as post-surgery pain or pain from cancer. These drugs work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. Common opioids include morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.-
Morphine: Often used in hospital settings for acute pain.
-
Oxycodone (OxyContin): Prescribed for chronic pain conditions.
-
Hydrocodone: Often combined with acetaminophen for stronger pain relief.
Warning: Opioids can be addictive, and their use should be closely monitored by a healthcare professional.
-
-
Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants
Some antidepressants and anticonvulsants can help manage nerve pain. These medications are often used for conditions like fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy, or postherpetic neuralgia.-
Amitriptyline: A tricyclic antidepressant used for nerve pain.
-
Gabapentin (Neurontin): An anticonvulsant that helps alleviate nerve-related pain.
-
-
Topical Pain Relievers
Topical treatments like creams, gels, and patches are used to relieve localized pain. These are applied directly to the skin and can provide targeted relief for muscle and joint pain.-
Lidocaine patches: Numb the area and reduce pain sensation.
-
Capsaicin creams: Help reduce pain by depleting substance P, a chemical involved in sending pain signals.
-

How Do Pain Management Drugs Work?
Pain management drugs typically work by altering the way the body perceives or processes pain. Here’s a breakdown of how different medications function:
-
Blocking Pain Signals
NSAIDs and acetaminophen reduce pain by inhibiting the production of chemicals like prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation. By blocking these chemicals, the pain response is lessened. -
Altering the Brain’s Pain Perception
Medications like opioids work by interacting with receptors in the brain, reducing the sensation of pain. While effective, opioids come with significant risks, including addiction and overdose. -
Nerve Modulation
Antidepressants and anticonvulsants can modify the way nerves transmit pain signals to the brain. These are particularly useful for chronic pain conditions that involve nerve damage or irritation. -
Local Numbing
Topical medications like lidocaine provide localized numbing at the site of pain. These are ideal for treating injuries or conditions that affect a specific area of the body.
Benefits of Pain Management Drugs
Using the right pain management drugs can significantly improve a person’s quality of life. Here are some benefits:
-
Immediate Pain Relief: Many pain medications provide quick relief, allowing you to return to your normal activities.
-
Effective for Chronic Pain: Certain medications, such as opioids or antidepressants, are effective for managing chronic pain conditions.
-
Improved Functionality: By alleviating pain, these drugs help individuals function better in their daily lives, improving mobility and reducing stress.
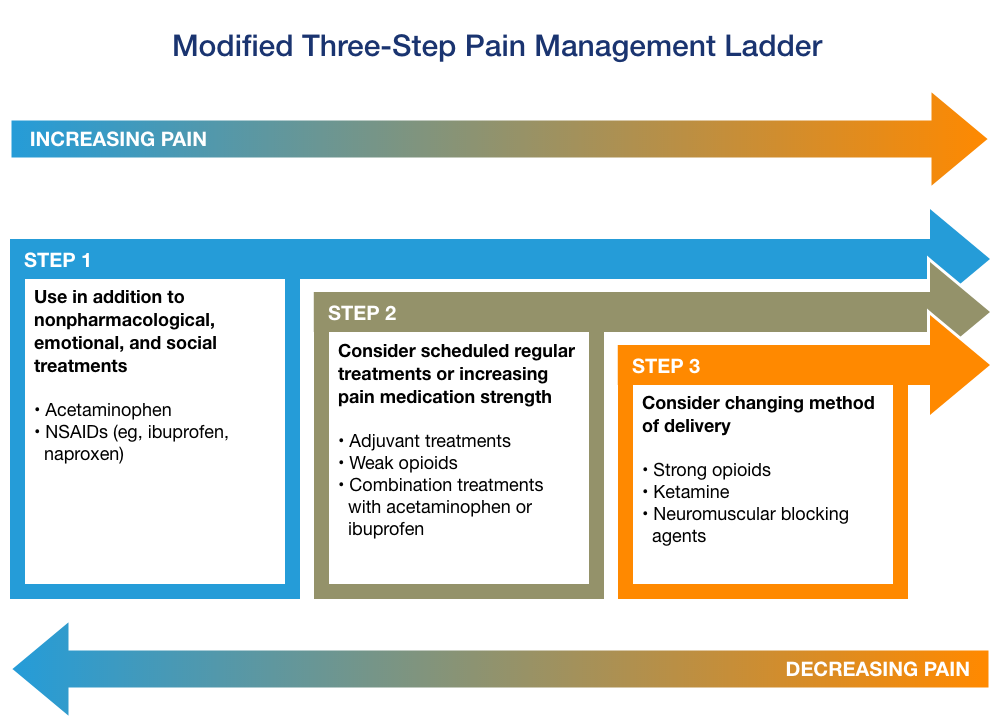
Pain Management Ladder
One of the strategies used in pain management is the “pain management ladder,” which helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate medication based on pain severity. The ladder consists of three steps:
-
Step 1: Non-opioid medications like NSAIDs or acetaminophen for mild pain.
-
Step 2: Mild opioids, combined with non-opioid medications, for moderate pain.
-
Step 3: Strong opioids or other prescription drugs for severe pain.
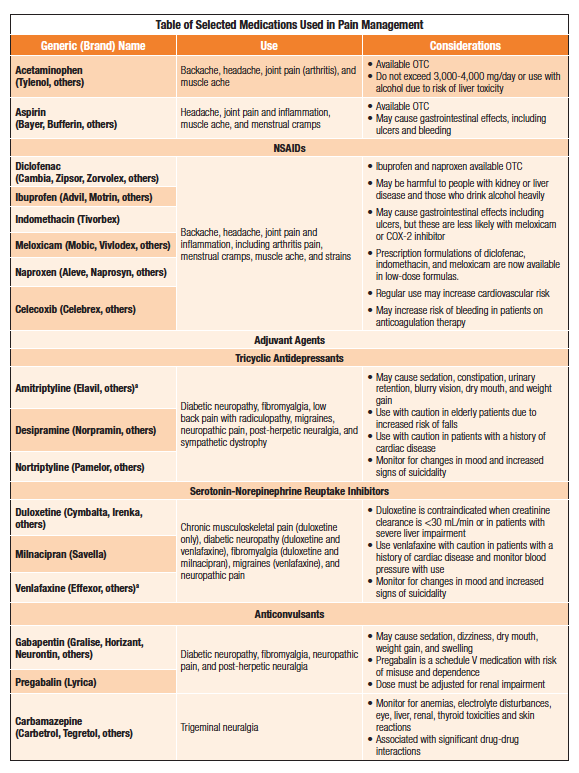
Safety and Considerations
While pain management drugs can be highly effective, they should be used with caution. Here are some key safety tips:
-
Follow Dosage Recommendations: Always adhere to the prescribed or recommended dosage. Overuse can lead to serious side effects, such as liver damage (with acetaminophen) or gastrointestinal bleeding (with NSAIDs).
-
Consult with a Healthcare Provider: If you experience side effects or if pain persists despite treatment, speak with your doctor. They may adjust your medication or suggest alternative treatments.
-
Monitor for Side Effects: Common side effects of pain medications can include nausea, dizziness, or stomach irritation. Be aware of any adverse reactions and report them to your doctor.
-
Be Aware of Addiction Risks: Opioids can be highly addictive, so they should only be used as directed by a healthcare professional. If you are concerned about addiction, ask your doctor about alternative pain management options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I know which pain medication is right for me?
The type of pain management drug best suited to you will depend on the type, severity, and duration of your pain. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate medication based on your specific needs.
2. Are there natural alternatives to pain management drugs?
Yes, many people turn to natural pain relief methods like acupuncture, physical therapy, or herbal supplements. While these may not be as fast-acting as medications, they can be effective for managing chronic pain.
3. Can pain management drugs cause long-term side effects?
Long-term use of pain medications, especially opioids or NSAIDs, can lead to complications like stomach ulcers, kidney damage, or dependence. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor usage and minimize risks.
4. What should I do if my pain medication isn’t working?
If your medication isn’t providing relief, consult your doctor. They may adjust the dosage, switch medications, or explore other pain management options.
5. Can I combine pain medications?
Combining medications like NSAIDs and acetaminophen can be effective for managing pain. However, always consult with your doctor before combining medications to avoid harmful interactions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right pain management drugs is essential for effective pain relief. Whether you’re dealing with acute pain from an injury or chronic pain from a medical condition, understanding the available treatments and their risks can help you make informed decisions. Always use pain medications as directed and consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any issues. With the right approach, you can manage your pain and improve your quality of life.
For more information on pain management strategies, visit our Pain Management Guide.